When you’re evaluating pump options for your operation, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits of gear pumps against other types. Gear pumps offer consistent flow and handle high-viscosity fluids effectively, but that’s just one piece of the puzzle. Consider how centrifugal, diaphragm, and screw pumps could meet different needs within your system. Each type has unique strengths and weaknesses, and the right choice hinges on your specific requirements. So, which pump will truly serve your operation best? Let’s explore the factors that could influence your decision.
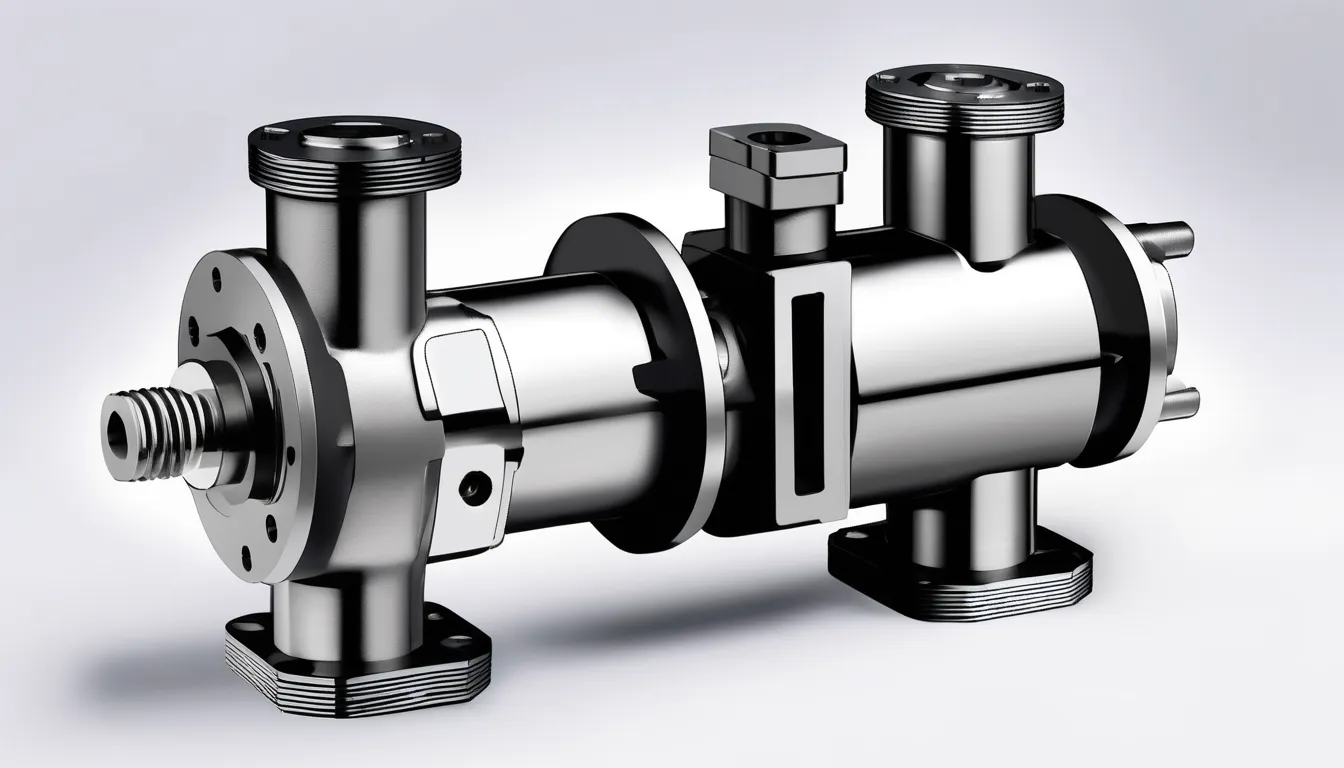
Overview of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps play a crucial role in various industrial applications by efficiently transferring fluids. These pumps utilize a pair of interlocking gears to move fluids through the system. As the gears rotate, they create a vacuum that draws in the fluid and then pushes it out under pressure, ensuring a consistent flow rate.
You’ll find gear pumps commonly used in hydraulic systems, fuel transfer, and lubricant applications due to their ability to handle high viscosity fluids effectively.
One of the key features of gear pumps is their design, which typically includes an inlet and outlet port, allowing for easy installation and integration into existing systems. They can be configured in various ways, such as internal and external gear designs, each serving specific applications.
When choosing a gear pump, consider factors like flow rate, pressure requirements, and fluid characteristics. Understanding these parameters helps you select the right pump for your needs.
Additionally, keep in mind maintenance aspects, as regular checks can ensure optimal performance and longevity. Overall, gear pumps are a reliable choice for many operations, providing efficiency and durability in fluid transfer applications.
Advantages of Gear Pumps
When considering pump options for your application, the advantages of gear pumps become clear. These pumps are known for their efficiency, providing a consistent flow rate with minimal pulsation. This characteristic is crucial when you need precise delivery of fluids, especially in industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals.
Another major benefit is their ability to handle a wide range of viscosities. Whether you’re working with thin oils or thick slurries, gear pumps can manage the flow effectively, making them versatile for various applications.
Their simple design also means fewer moving parts, which translates to reduced maintenance and lower operational costs.
You’ll also appreciate the compact size of gear pumps. They can fit easily into tight spaces, allowing for flexible installation options. Additionally, gear pumps operate quietly, which can be a significant advantage in environments where noise reduction is essential.
Lastly, their robust construction ensures durability, providing reliable performance over time. This reliability minimizes downtime and enhances productivity in your operation.
Common Types of Pumps
Pumps come in various types, each designed to meet specific needs across different industries.
You’ll often encounter centrifugal pumps, which use a rotating impeller to move fluids efficiently, making them ideal for applications like water supply and heating.
If you’re handling viscous liquids, positive displacement پمپ دنده ای s might be your go-to choice. These pumps push fluid through a chamber and ensure a consistent flow rate, regardless of pressure changes.
Diaphragm pumps are another common type, utilizing a flexible diaphragm to create a vacuum that draws in and expels fluid. They’re particularly useful for handling corrosive or abrasive materials.
If your operation involves high-pressure needs, consider using screw pumps, which deliver a smooth, continuous flow by using two or more screws to transport the fluid.
Lastly, you might see submersible pumps in wastewater management. These pumps are designed to operate underwater, effectively moving waste and water from lower levels to the surface.
Understanding these common types will help you select the right pump for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in your operations.
Comparing Pump Performance
Understanding the various types of pumps lays the groundwork for comparing their performance in real-world applications. When evaluating pump performance, consider several critical factors that influence efficiency and suitability for your specific needs.
Each pump type, whether gear, diaphragm, or centrifugal, has distinct characteristics that affect how well it operates under different conditions.
Here are some key performance factors to consider:
- Flow Rate: Measure how much fluid a pump can move over a set time.
- Pressure Range: Understand the maximum pressure a pump can handle without failure.
- Viscosity Handling: Determine how well the pump can manage fluids with varying thickness.
- Energy Efficiency: Evaluate how much power the pump consumes relative to its output.
- Maintenance Needs: Consider the frequency and complexity of required maintenance tasks.
Selecting the Right Pump
Choosing the right pump for your application can significantly impact efficiency and performance, especially since each type has unique strengths and weaknesses.
Start by assessing your specific needs, including the fluid’s viscosity, temperature, and pressure requirements. For high-viscosity fluids, gear pumps are often the best choice due to their ability to handle thicker materials without losing efficiency.
Next, consider the flow rate you require. If you’re dealing with varying flow demands, a centrifugal pump might be more suitable, as it can adapt to changes in fluid dynamics better than a gear pump.
Additionally, think about maintenance and operational costs. Gear pumps tend to have lower maintenance needs, but they mightn’t be the most cost-effective choice for every situation.
Don’t forget to evaluate the installation space and orientation. Some pumps require specific arrangements, and choosing one that fits your layout can save you time and hassle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right pump for your operation really boils down to your specific needs. Gear pumps shine when dealing with high-viscosity fluids and offer a steady flow, making them perfect for hydraulic and fuel transfer tasks. However, if your application demands flexibility or unique handling requirements, other pump types might suit you better. Assess your operational demands, and you’ll find the pump that fits seamlessly into your process.