In the ever-evolving world of computer storage, Solid State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) represent the two primary options available to consumers. While HDDs have been a reliable choice for many years, SSDs have increasingly become the preferred option for those seeking faster performance and enhanced efficiency. This article explores the numerous benefits of SSDs over HDDs, highlighting why many users are making the switch.
Speed and Performance
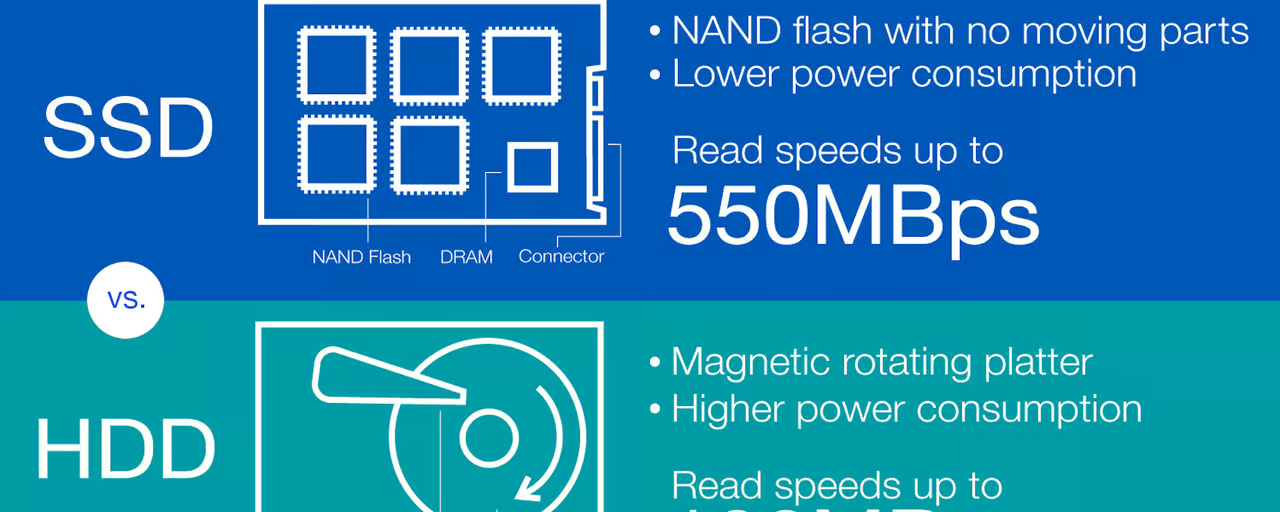
One of the most compelling reasons to choose an SSD over an HDD is the significant difference in speed and performance. SSDs utilize flash memory to store data, which allows them to access and transfer information much more quickly than HDDs. Unlike HDDs, which rely on spinning disks and read/write heads to access data, SSDs have no moving parts. This absence of mechanical components translates into faster data access times and quicker boot-ups, application launches, and file transfers.
For users who require high-performance computing, such as gamers, video editors, and professionals working with large datasets, SSDs provide a noticeable boost in speed. This improved performance can lead to a more efficient workflow and a smoother overall experience.
Durability and Reliability
Another advantage of SSDs is their durability and reliability compared to HDDs. The lack of moving parts in SSDs means there is less risk of mechanical failure. HDDs, on the other hand, are prone to wear and tear due to their spinning disks and read/write heads. These mechanical components are susceptible to damage from shocks, vibrations, and physical impacts.
Because SSDs are more resistant to physical damage, they are often preferred in portable devices like laptops and external drives, where movement and handling can be more frequent. This increased durability can result in a longer lifespan for SSDs and a reduced risk of data loss due to hardware failure.
Power Efficiency
Power efficiency is another area where SSDs have a clear advantage over HDDs. SSDs generally consume less power because they lack the mechanical components that require energy to operate. This reduced power consumption can lead to longer battery life in laptops and a lower overall energy footprint for desktop computers.
For users who prioritize energy efficiency or are concerned about their carbon footprint, the choice of an SSD can contribute to a more environmentally friendly computing experience. Additionally, the lower power requirements can help reduce cooling needs and decrease overall system noise.
Noise and Heat Reduction
The absence of moving parts in SSDs also means that they operate silently. HDDs, with their spinning disks and moving read/write heads, can generate noticeable noise during operation. For users who value a quiet working environment or are sensitive to noise, SSDs offer a significant advantage by providing a noiseless experience.
Furthermore, SSDs produce less heat compared to HDDs. The reduced heat output can contribute to a cooler operating environment within a computer, which can, in turn, benefit other components by reducing thermal stress and potential overheating issues.
Size and Form Factor Flexibility
SSDs come in a variety of sizes and form factors, offering greater flexibility in terms of installation and integration. Unlike HDDs, which are typically larger and require more space, SSDs can be found in compact sizes that are ideal for slim laptops and ultrabooks. This flexibility allows users to choose an SSD that fits their specific needs and design preferences.
Additionally, the compact nature of SSDs makes them well-suited for use in small form factor PCs and specialized applications where space is at a premium. This versatility can enhance the overall design and functionality of computing devices.
Cost Considerations
Historically, SSDs have been more expensive per gigabyte compared to HDDs. However, as technology advances and manufacturing processes improve, the price gap between SSDs and HDDs has been narrowing. While SSDs may still come with a higher upfront cost, their benefits in terms of performance, durability, and efficiency often outweigh the price difference for many users.
As SSD technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, the cost-benefit ratio of SSDs is expected to improve further, making them a more attractive option for a wider range of users.
Conclusion
In summary, the advantages of SSDs over HDDs are clear. With their superior speed and performance, increased durability and reliability, power efficiency, noise and heat reduction, and flexible form factors, SSDs offer a compelling case for upgrading from traditional HDDs. While cost considerations may still play a role in decision-making, the numerous benefits of SSDs make them a worthwhile investment for anyone seeking a more efficient and reliable computing experience.